A taste of our 2016 harvest
-
Radical route for the synthesis of chiral molecules
Prof. Paolo Melchiorre’s group developed a new methodology for the selective formation of chiral molecules. The work, published in Nature, combines two strategies which require very mild reaction conditions –enantioselective iminium ion chemistry and photoredox catalysis- to set quaternary carbon stereocentres with high enantioselectivity. The work represents a breakthrough in the synthesis of chiral molecules as it manages to perform the selective synthesis of the desired molecule via a new radical route that combines the action of a photocatalyst activated by visible light with a chiral organic catalyst. (Read more)
Asymmetric catalytic formation of quaternary carbons by iminium ion trapping of radicals
J. J. Murphy, D. Bastida, S. Paria, M. Fagnoni, P. Melchiorre
Nature, 2016, 532, 218-222 -
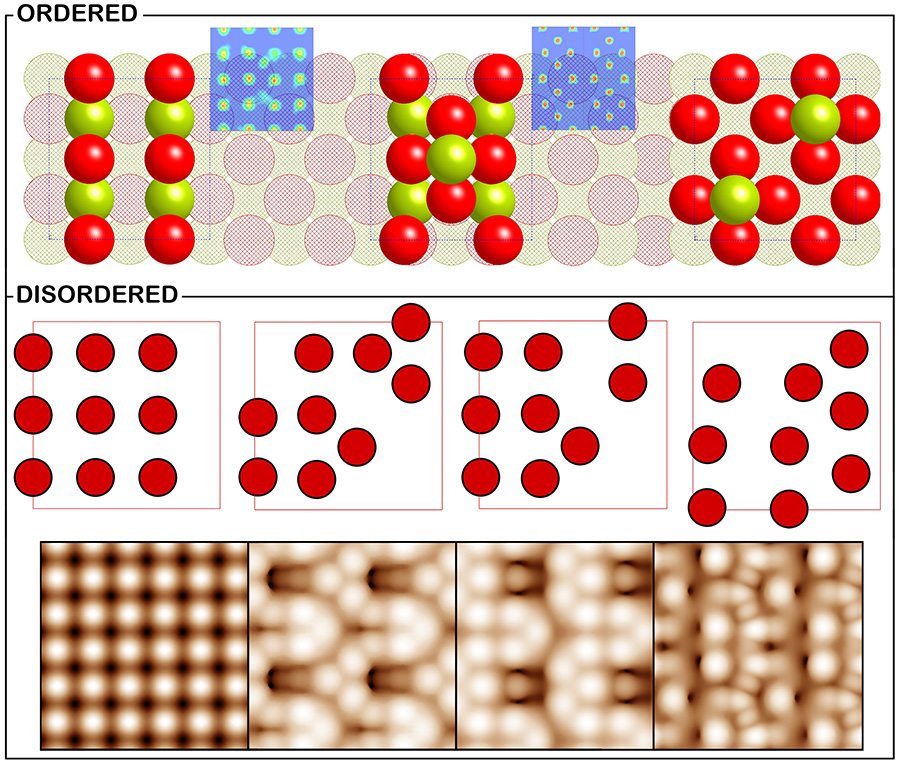
Calculations predict disorder in the surface of certain materials
The group of Professor Núria López published a paper in Nature Materials explaining how massive simulations prove that certain surfaces are more disordered than previously thought. DFT calculations –more than 50000 simulations– carried out on the Mare Nostrum supercomputer at the Barcelona Supercomputing Center allow the introduction of all the complexity in these systems.
Based on the concept of configurational entropy, ICIQ researchers could classify different surface rearrangements according to their stability. They also demonstrated that CeO2 surfaces are dynamic and the rearrangements are interchangeable. The new terminations show different patterns on the materials surface, affecting their mechanical and catalytic properties and their properties as sensors. (Read more)
Entropic contributions enhance polarity compensation for CeO2(100) surfaces
M. Capdevila-Cortada and Núria López.
Nat. Mater., 2016, DOI: 10.1038/NMAT4804. -
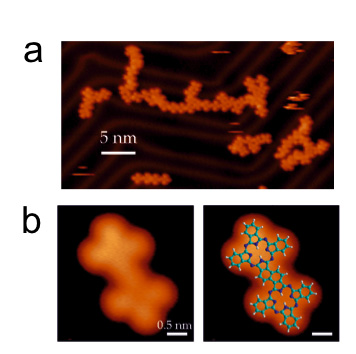
New reaction for the synthesis of nanostructures
The collaboration between the research groups of professors Pau Ballester and José Ramón Galán-Mascarós at ICIQ and the group of Dr. David Ecija at Institute IMDEA Nanoscience allowed the development of a new chemical reaction for the synthesis of low-dimensional polymers that can be rationalized as phthalocyanine derivatives. The results obtained were published in Nature Communications.
Surface-mediated synthesis of low-dimensional polymers from simple molecular precursors is a rapidly emerging field. In this work, the researchers introduce surface-confined thermally tunable reaction pathways as a route to select intramolecular versus intermolecular reactions yielding either monomeric phthalocyanines or low-dimensional phthalocyanine polymers, respectively. (Read more)
Thermal selectivity of intermolecular versus intramolecular reactions on surfaces
B. Cirera, N. Giménez-Agulló, J. Björk, F. Martínez-Peña, A. Martin-jimenez, J. Rodríguez-Fernandez, A. M. Pizarro, R. Otero, J. M. Gallego, P. Ballester, J. R. Galán-Mascarós, D. Ecija
Nature Communications, 2016, 7, 11002.